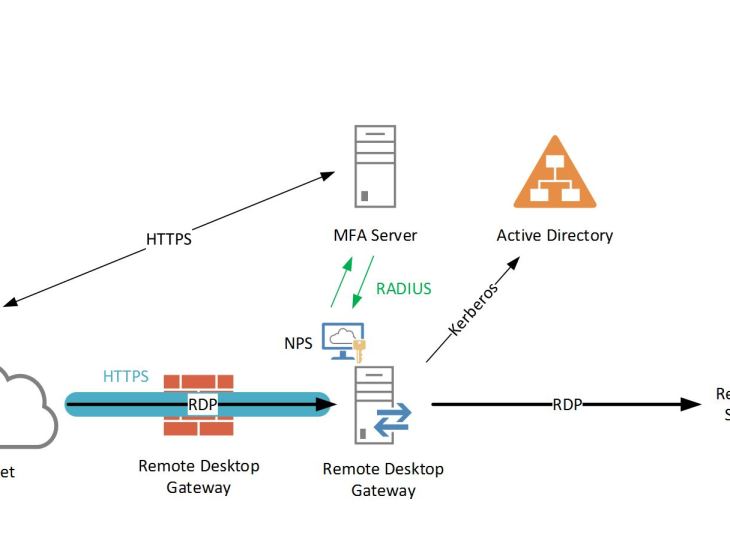
Azure MFA communicates with Azure AD, retrieves the user’s details, and performs the secondary authentication using the method configured by the user (text message, mobile app, and so on). Upon success of the MFA challenge, Azure MFA communicates the result to the NPS extension. We need to set up multi factor authentication when connecting to server using RDP. I have tried Azure MFA Server, but it gives so much troubles. Maybe anyone have some information about this or practice with this kind of things. Thank you in advance.
Remote Desktop Service and Azure AD Application Proxy work together to improve the productivity of workers who are away from the corporate network.
The intended audience for this article is:
- Current Application Proxy customers who want to offer more applications to their end users by publishing on-premises applications through Remote Desktop Services.
- Current Remote Desktop Services customers who want to reduce the attack surface of their deployment by using Azure AD Application Proxy. This scenario gives a set of two-step verification and Conditional Access controls to RDS.
How Application Proxy fits in the standard RDS deployment
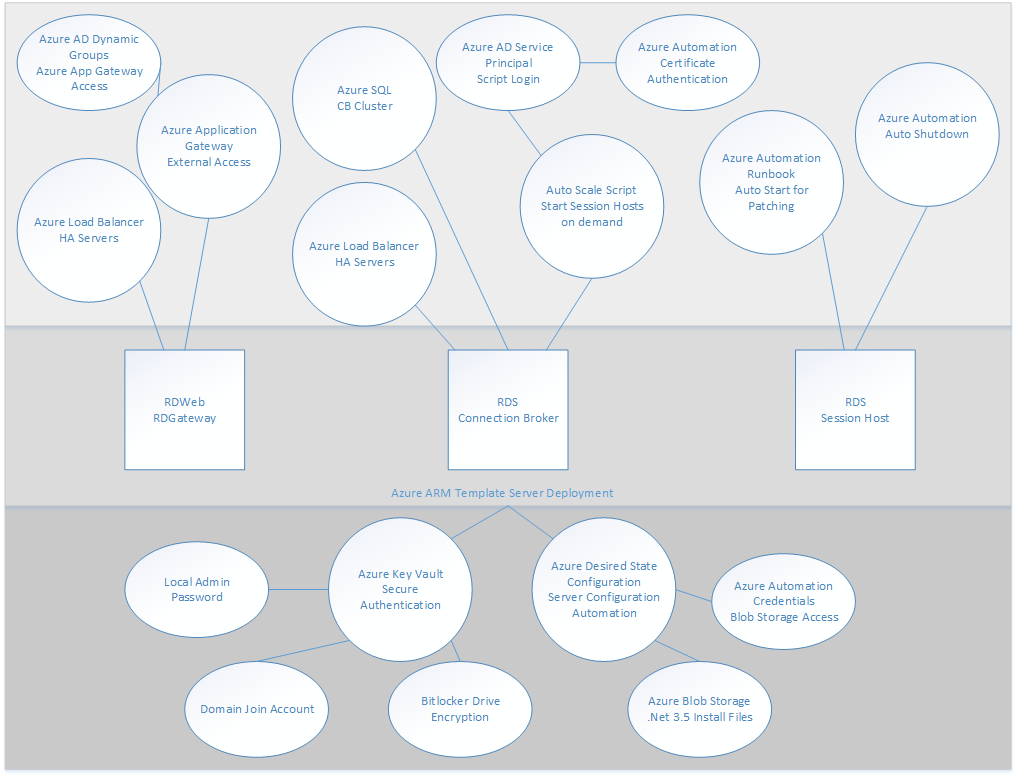
A standard RDS deployment includes various Remote Desktop role services running on Windows Server. Looking at the Remote Desktop Services architecture, there are multiple deployment options. Unlike other RDS deployment options, the RDS deployment with Azure AD Application Proxy (shown in the following diagram) has a permanent outbound connection from the server running the connector service. Other deployments leave open inbound connections through a load balancer.
In an RDS deployment, the RD Web role and the RD Gateway role run on Internet-facing machines. These endpoints are exposed for the following reasons:
- RD Web provides the user a public endpoint to sign in and view the various on-premises applications and desktops they can access. Upon selecting a resource, an RDP connection is created using the native app on the OS.
- RD Gateway comes into the picture once a user launches the RDP connection. The RD Gateway handles encrypted RDP traffic coming over the internet and translates it to the on-premises server that the user is connecting to. In this scenario, the traffic the RD Gateway is receiving comes from the Azure AD Application Proxy.
Tip
If you haven't deployed RDS before, or want more information before you begin, learn how to seamlessly deploy RDS with Azure Resource Manager and Azure Marketplace.
Requirements
Azure Mfa For Rdp Free
- Both the RD Web and RD Gateway endpoints must be located on the same machine, and with a common root. RD Web and RD Gateway are published as a single application with Application Proxy so that you can have a single sign-on experience between the two applications.
- You should already have deployed RDS, and enabled Application Proxy. Ensure you have satisfied the pre-requisites to enable Application Proxy, such as installing the connector, opening required ports and URLS, and enabling TLS 1.2 on the server.
- Your end users must use a compatible browser to connect to RD Web or the RD Web client. For more details see Support for client configurations.
- When publishing RD Web, it is recommended to use the same internal and external FQDN. If the internal and external FQDNs are different then you should disable Request Header Translation to avoid the client receiving invalid links.
- If you are using RD Web on Internet Explorer, you will need to enable the RDS ActiveX add-on.
- If you are using the RD Web client, you will need to use the Application Proxy connector version 1.5.1975 or later.
- For the Azure AD pre-authentication flow, users can only connect to resources published to them in the RemoteApp and Desktops pane. Users can't connect to a desktop using the Connect to a remote PC pane.
- If you are using Windows Server 2019, you may need to disable HTTP2 protocol. For more information, see Tutorial: Add an on-premises application for remote access through Application Proxy in Azure Active Directory.
Deploy the joint RDS and Application Proxy scenario
After setting up RDS and Azure AD Application Proxy for your environment, follow the steps to combine the two solutions. These steps walk through publishing the two web-facing RDS endpoints (RD Web and RD Gateway) as applications, and then directing traffic on your RDS to go through Application Proxy.
Publish the RD host endpoint
Publish a new Application Proxy application with the following values:
- Internal URL:
https://<rdhost>.com/, where<rdhost>is the common root that RD Web and RD Gateway share. - External URL: This field is automatically populated based on the name of the application, but you can modify it. Your users will go to this URL when they access RDS.
- Preauthentication method: Azure Active Directory
- Translate URL headers: No
- Internal URL:
Assign users to the published RD application. Make sure they all have access to RDS, too.
Leave the single sign-on method for the application as Azure AD single sign-on disabled.
Note
Your users are asked to authenticate once to Azure AD and once to RD Web, but they have single sign-on to RD Gateway.
Select Azure Active Directory, and then App Registrations. Choose your app from the list.
Under Manage, select Branding.
Update the Home page URL field to point to your RD Web endpoint (like
https://<rdhost>.com/RDWeb).
Direct RDS traffic to Application Proxy
Connect to the RDS deployment as an administrator and change the RD Gateway server name for the deployment. This configuration ensures that connections go through the Azure AD Application Proxy service.
Connect to the RDS server running the RD Connection Broker role.
Launch Server Manager.
Select Remote Desktop Services from the pane on the left.
Select Overview.
In the Deployment Overview section, select the drop-down menu and choose Edit deployment properties.
In the RD Gateway tab, change the Server name field to the External URL that you set for the RD host endpoint in Application Proxy.
Change the Logon method field to Password Authentication.
Run this command for each collection. Replace <yourcollectionname> and <proxyfrontendurl> with your own information. This command enables single sign-on between RD Web and RD Gateway, and optimizes performance:
For example:
Note
The above command uses a backtick in '`nrequire'.
To verify the modification of the custom RDP properties as well as view the RDP file contents that will be downloaded from RDWeb for this collection, run the following command:
Now that you've configured Remote Desktop, Azure AD Application Proxy has taken over as the internet-facing component of RDS. You can remove the other public internet-facing endpoints on your RD Web and RD Gateway machines.
Enable the RD Web Client
If you also want users to be able to use the RD Web Client follow steps at Set up the Remote Desktop web client for your users to enable this.
The Remote Desktop web client lets users access your organization's Remote Desktop infrastructure through a HTML5-compatible web browser such as Microsoft Edge, Internet Explorer 11, Google Chrome, Safari, or Mozilla Firefox (v55.0 and later).
Test the scenario
Test the scenario with Internet Explorer on a Windows 7 or 10 computer.

- Go to the external URL you set up, or find your application in the MyApps panel.
- You are asked to authenticate to Azure Active Directory. Use an account that you assigned to the application.
- You are asked to authenticate to RD Web.
- Once your RDS authentication succeeds, you can select the desktop or application you want, and start working.
Support for other client configurations
The configuration outlined in this article is for access to RDS via RD Web or the RD Web Client. If you need to, however, you can support other operating systems or browsers. The difference is in the authentication method that you use.
| Authentication method | Supported client configuration |
|---|---|
| Pre-authentication | RD Web- Windows 7/10 using Internet Explorer* or Edge Chromium IE mode + RDS ActiveX add-on |
| Pre-authentication | RD Web Client- HTML5-compatible web browser such as Microsoft Edge, Internet Explorer 11, Google Chrome, Safari, or Mozilla Firefox (v55.0 and later) |
| Passthrough | Any other operating system that supports the Microsoft Remote Desktop application |
*Edge Chromium IE mode is required when the My Apps portal is used for accessing the Remote Desktop app.
The pre-authentication flow offers more security benefits than the passthrough flow. With pre-authentication you can use Azure AD authentication features like single sign-on, Conditional Access, and two-step verification for your on-premises resources. You also ensure that only authenticated traffic reaches your network.
To use passthrough authentication, there are just two modifications to the steps listed in this article:
- In Publish the RD host endpoint step 1, set the Preauthentication method to Passthrough.
- In Direct RDS traffic to Application Proxy, skip step 8 entirely.
Next steps
Are you implementing Microsoft Azure Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) in your Remote Desktop Services/RemoteApp (RDS) deployments? You better be….
Don’t Put Mobility Ahead of Security. You Can Have Both!
As the business landscape continues to evolve and “mobility” becomes less of a buzzword and more of a necessity, many companies are implementing mobile first and Bring-Your-Own-Device (BYOD) IT strategies to alleviate expensive hardware costs and rents. An added bonus – it gives employees the autonomy to fully execute their job functions.
A widely used solution, and one of the most popular mobile infrastructure deployments, Microsoft Remote Desktop Services provides users remote access to company owned Windows virtual desktops, data, and applications from almost any device. Users simply log in using the Remote Desktop Client from a preferred device and gain secure access to the corporate assets they need to perform their duties.
Whether you are deploying your Microsoft Remote Desktop Services environment on-premises, to the Microsoft Azure Cloud, or your preferred Datacenter, Microsoft RDS is the platform of choice for building virtualization solutions for every business.

But how do you protect corporate assets and your user credentials from being stolen when using RDS?
Add a little salt to those AD credentials.
Is authenticating using Active Directory 100% secure? The short answer is no. Although AD provides a layer of security to your credentials, even an amateur hacker using specialized tools can quickly gain access to AD credentials.
In the best-case scenario, a hacker will be able to gain access to your RDS deployment and sensitive data. In some cases, a sophisticated hacker will use a service attack to gain admin credentials, giving the hacker access to your company network and even control over user domain. Both scenarios are considered a data breach and put your company in harm’s way.
Average cost of a data breach in 2018.
According to the 12th annual Cost of Data Breach Study, the average cost of data breach is $3.62 million with an average per stolen record cost of $141. Simply put, a data breach can cripple your business even if you are able to survive it at all.
What is Azure MFA?
Microsoft Azure Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is Microsoft’s two-step verification solution, a crucial step in protecting your RDS. Two-step verification is a process of authentication that requires more than one verification method and adds a critical second layer of security to user sign-ins. Azure MFA helps safeguard access to data and applications while meeting user demand for an easy sign-in process. It delivers strong authentication across a range of verification methods, including phone calls, text messages, and mobile app verifications.
Azure MFA is an easy to use and reliable solution that provides an extra layer of security to protect users and your data.
Make Microsoft Azure MFA Standard Across all Your RDS Deployments
Although Microsoft Azure Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) provides an inexpensive, easy to deploy, and necessary layer of security to your RDS environments.
With Azure MFA successfully deployed, users and admins attempting to connect to company resources via the Remote Desktop Client will be prompted to enter a 6-digit code as a second layer of authentication to connect. This code is delivered automatically to the user’s mobile device, by either a phone call, text, or mobile app verification, after AD credentials are entered.
Azure Mfa Server For Rdp
Hackers may still be able to get a hold of your AD credentials; however, with MFA deployed, without access to your phone or network, their efforts are essentially useless.
Azure Mfa For Rdp Service
Full proof? Not quite. Is it necessary? Absolutely.
Where can you purchase Microsoft Azure MFA Licenses?
Azure Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is usually purchased through an Office 365 subscription as Azure Active Directory Premium or included in a bundled plan.
Our recommendation would be to purchase a license through a CSP partner like Total Cloud IT as part of the Enterprise Mobility + Security bundle. The. Enterprise Mobility + Security includes numerous security tools necessary to protect your data on-premises or in the Cloud.
Need Deployment help?
Total Cloud IT is a Microsoft CSP Partner specializing in Office 365 and Azure Enterprise Deployments.
Purchasing and implementing the right solution can be a tricky endeavor. Let Total Cloud IT take the guess work out of the equation.
Azure Mfa Rds Gateway
Please contact joel@totalcloudit.com for a free consultation and get your business on the path to security.
Azure Mfa Rdp 2012 R2
My name is Joel McElroy. I’ve been thinking about data security, you should be too.
